一、了解太陽能光伏 (PV) 發電
了解并網和離網光伏系統配置以及每種類型涉及的基本組件。
太陽能光伏發電是使用太陽能電池板將來自太陽的能量轉換為電能的過程。太陽能電池板,也稱為光伏電池板,在光伏系統中組合成陣列。光伏系統也可以安裝在并網或離網(獨立)配置中。這兩種光伏系統配置的基本組件包括太陽能電池板、匯流箱、逆變器、優化器和斷開器。并網光伏系統還可能包括儀表、電池、充電控制器和電池斷開器。太陽能光伏發電有幾個優點和缺點(見表 1)。
1、太陽能光伏 (PV) 發電優點缺點
?陽光是免費的,在該國的許多地區很容易獲得。?光伏系統初始投資高。
?光伏系統不會產生有毒氣體排放、溫室氣體或噪音。?光伏系統需要大面積發電。
?光伏系統沒有活動部件。?日照量可能會有所不同。
?光伏系統減少對石油的依賴。?當系統無法提供全部容量時,光伏系統需要額外的能量存儲或訪問其他資源,如公用電網。
?光伏系統能夠在未連接到電網的偏遠地區發電。
?并網光伏系統可以減少電費。
表 1.太陽能光伏發電有優缺點。
2、并網光伏系統
光伏系統最常采用并網配置,因為與依賴電池的離網光伏系統相比,它更易于設計且通常更便宜。并網光伏系統允許房主從電網消耗更少的電力,并將未使用或多余的電力提供回公用電網(見圖 2)。系統的應用將決定系統的配置和規模。例如,住宅并網光伏系統的額定功率小于 20 kW,商業系統的額定功率為 20 kW 至 1MW,而公用事業儲能系統的額定功率大于 1MW。
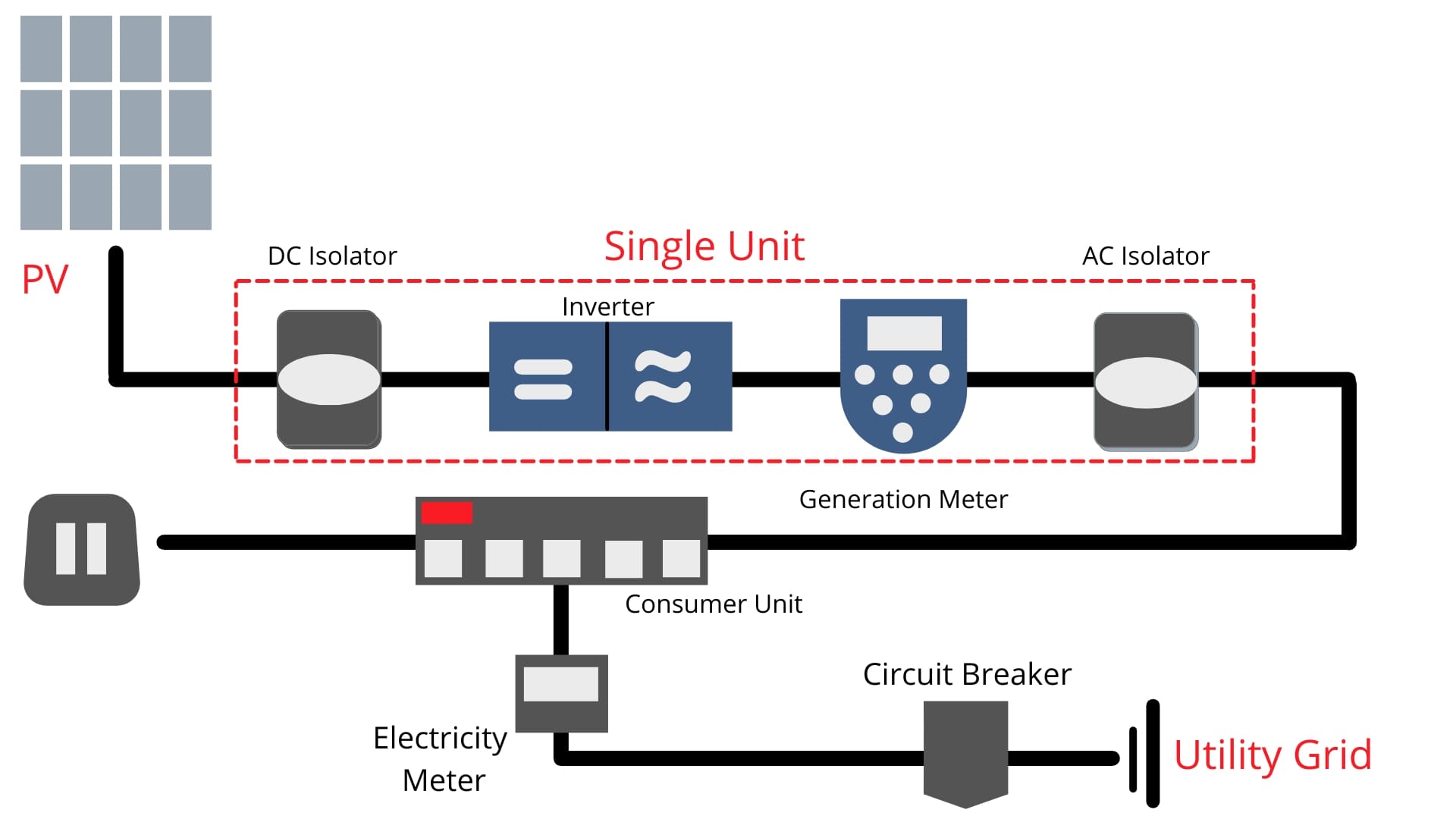
圖 2.光伏系統的常見配置是沒有備用電池的并網光伏系統。
3、離網(獨立)光伏系統
離網(獨立)光伏系統在白天使用太陽能電池板陣列為可充電電池組充電,以便在無法獲得太陽能的夜間使用。使用離網光伏系統的原因包括降低能源成本和停電、生產清潔能源和能源獨立。離網光伏系統包括電池組、逆變器、充電控制器、電池斷開器和可選發電機。
4、太陽能板
光伏系統中使用的太陽能電池板是太陽能電池的組件,通常由硅組成,通常安裝在剛性平面框架中。太陽能電池板串聯在一起形成串,太陽能電池板串并聯形成陣列。太陽能電池板按其產生的直流電量進行評級。應定期檢查太陽能電池板以清除污垢、碎屑或雪,并檢查電氣連接。
由于光伏受到陰影的不利影響,任何陰影都會顯著降低太陽能電池板的功率輸出。太陽能電池板的性能會有所不同,但在大多數情況下,保證的功率輸出預期壽命在 10 年到 25 年之間。太陽能電池板的功率輸出以瓦特為單位。在理想的陽光和溫度條件下,額定功率輸出范圍為 200 W 至 350 W。
5、太陽能電池陣列的構造和安裝
當太陽能電池板安裝在物業上時,它們必須以一定角度安裝以最好地接收陽光。典型的太陽能電池陣列支架包括屋頂、獨立式和定向跟蹤支架(參見圖 4)。屋頂安裝的太陽能電池板可以與住宅的建筑融為一體,并將節省院子空間。
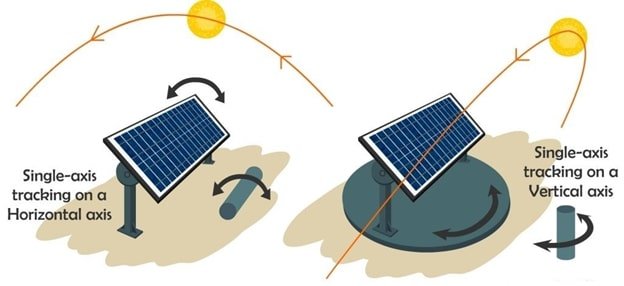
圖 4.典型的太陽能電池陣列支架包括屋頂、獨立式和屋頂或地面上的定向跟蹤支架。圖片由格林沙撈越提供
安裝在屋頂的太陽能電池陣列連接到屋頂椽子上,旨在處理與屋頂相同的力和氣候條件。復合瓦被認為是最容易安裝太陽能電池板的屋頂材料,而板巖和瓷磚屋頂材料通常被認為是最困難的。屋頂安裝的太陽能電池板的主要缺點是它們需要進行維護。
獨立式太陽能電池陣列可以設置在便于維護的高度。然而,獨立式太陽能電池陣列通常需要大量空間。此外,獨立式太陽能電池板不應安裝在積雪較多的地區的地面上。
太陽能陣列支架也可以是固定的或跟蹤的。固定式太陽能電池板通常安裝在屋頂或獨立式上,預先設置了高度和角度,不會隨太陽移動。定向跟蹤太陽能電池陣列隨太陽從東向西移動,并在太陽移動時調整其角度以保持最大曝光。定向跟蹤太陽能陣列可以將光伏系統的每日能量輸出從 25% 提高到 40%。然而,盡管增加了功率輸出,但由于安裝系統的復雜性,定向跟蹤陣列可能無法證明增加的成本是合理的。
6、光伏匯流箱
光伏匯流箱接收多個太陽能電池板串的輸出,并將該輸出合并到一個連接到逆變器的主電源中。光伏匯流箱通常安裝在太陽能電池板附近和逆變器之前。光伏匯流箱可以包括過流保護、浪涌保護、預接線保險絲座和預配置連接器,以便于安裝到逆變器。使用預接線連接器可以節省連接到逆變器的電線。光伏匯流箱應定期檢查是否有泄漏或連接松動。
并非每個光伏系統安裝都需要光伏匯流箱。例如,當只有兩串或三串太陽能電池板時,可能不需要匯流箱。在這些情況下,太陽能電池板串直接連接到逆變器。
7、光伏逆變器
逆變器是一種接收直流電并將其轉換為交流電的設備。光伏逆變器具有三個基本功能:將光伏面板的直流電轉換為交流電,確保產生的交流頻率保持在每秒 60 個周期,并將電壓波動降至最低。最常見的光伏逆變器是微型逆變器、組串式逆變器和功率優化器(見圖 5)。
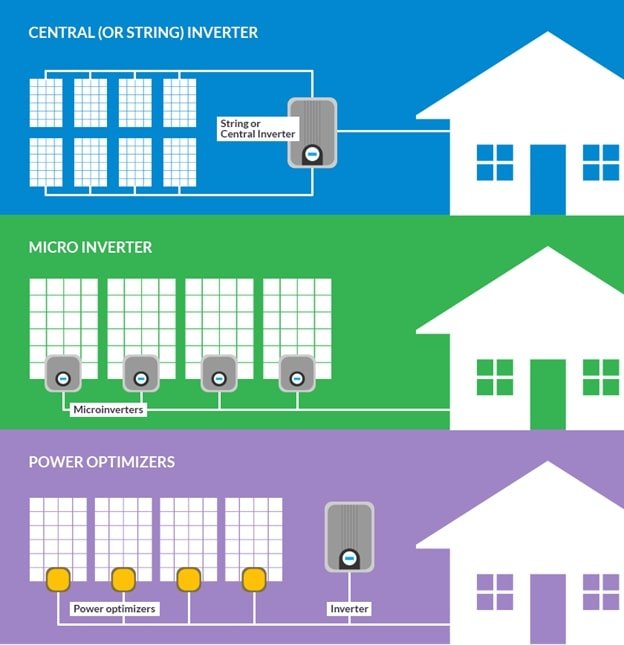
圖 5.微型逆變器連接到每個并聯的太陽能電池板,并將直流電直接轉換為交流電。串式逆變器與多個串聯的太陽能電池板一起使用。功率優化器安裝在每個并聯的太陽能電池板上。圖片由Letsgosolar提供
微型逆變器是將直流電轉換為交流電并直接安裝在單個太陽能電池板上的設備。因為直流到交流的轉換發生在每個太陽能電池板上,微型逆變器最大限度地提高了系統的潛在輸出。例如,如果一個太陽能電池板被一棵樹遮蔽,它不會影響任何其他太陽能電池板的輸出。微型逆變器還消除了對潛在危險的高壓直流接線的需求。
串式逆變器是一種將多個串聯太陽能電池板的直流電轉換為交流電的設備。然而,在串聯配置中,如果其中一個太陽能電池板停止發電,即使是由于臨時遮蔽,也會降低整個系統的性能。組串式逆變器處于高壓范圍(600 V 至 1000 V),用于大型光伏系統,沒有陰影問題。通常,住宅應用只需要一個組串式逆變器。
功率優化器(最大化器)是一種混合微型逆變器系統,可在將直流電發送到集中式逆變器之前對其進行調節,而不是將太陽能電池板的直流電直接轉換為交流電。當一個或多個面板被遮蔽或面板面向不同方向安裝時,功率優化器(如微型逆變器)仍然表現良好。功率優化器系統的成本往往高于串式逆變器系統,但低于微型逆變器系統。
8、光伏斷開器
自動和手動安全斷開器可保護光伏系統的接線和組件免受電涌和其他設備故障的影響。斷開連接確保光伏系統可以安全關閉,并且可以移除系統組件進行維護或維修。對于并網光伏系統,安全斷開裝置可確保發電設備與電網隔離,以確保公用事業人員的安全。光伏系統中的每個電源或儲能設備都需要斷開連接。交流斷開器通常安裝在主配電板之前的家中。公用事業通常需要一個可鎖定并安裝在公用事業儀表旁邊的外部交流斷開器,以便公用事業人員可以訪問它。
英文翻譯:
Learn about grid-connected and off-grid PV system configurations and the basic components involved in each kind.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation is the process of converting energy from the sun into electricity using solar panels. Solar panels, also called PV panels, are combined into arrays in a PV system. PV systems can also be installed in grid-connected or off-grid (stand-alone) configurations. The basic components of these two configurations of PV systems include solar panels, combiner boxes, inverters, optimizers, and disconnects. Grid-connected PV systems also may include meters, batteries, charge controllers, and battery disconnects. There are several advantages and disadvantages to solar PV power generation (see Table 1).
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
?Sunlight is free and readily available in many areas of the country. | ?PV systems have a high initial investment. |
?PV systems do not produce toxic gas emissions, greenhouse gases, or noise. | ?PV systems require large surface areas for electricity generation. |
?PV systems do not have moving parts. | ?The amount of sunlight can vary. |
?PV systems reduce dependence on oil. | ?PV systems require excess storage of energy or access to other sources, like the utility grid, when systems cannot provide full capacity. |
?PV systems have the ability to generate electricity in remote locations that are not linked to a grid. | |
?Grid-connected PV systems can reduce electric bills. |
Table 1. There are advantages and disadvantages to solar PV power generation.
Grid-Connected PV Systems
PV systems are most commonly in the grid-connected configuration because it is easier to design and typically less expensive compared to off-grid PV systems, which rely on batteries. Grid-connected PV systems allow homeowners to consume less power from the grid and supply unused or excess power back to the utility grid (see Figure 2). The application of the system will determine the system configuration and size. For example, residential grid-connected PV systems are rated less than 20 kW, commercial systems are rated from 20 kW to 1MW, and utility energy-storage systems are rated at more than 1MW.
Off-Grid (Stand-Alone) PV Systems
Off-grid (stand-alone) PV systems use arrays of solar panels to charge banks of rechargeable batteries during the day for use at night when energy from the sun is not available. The reasons for using an off-grid PV system include reduced energy costs and power outages, production of clean energy, and energy independence. Off-grid PV systems include battery banks, inverters, charge controllers, battery disconnects, and optional generators.
Solar Panels
Solar panels used in PV systems are assemblies of solar cells, typically composed of silicon and commonly mounted in a rigid flat frame. Solar panels are wired together in series to form strings, and strings of solar panels are wired in parallel to form arrays. Solar panels are rated by the amount of DC that they produce. Solar panels should be inspected periodically to remove dirt, debris, or snow, as well as to check electrical connections.
Since photovoltaics are adversely affected by shade, any shadow can significantly reduce the power output of a solar panel. The performance of a solar panel will vary, but in most cases, guaranteed power output life expectancy is between 10 years and 25 years. Solar panel power output is measured in watts. Power output ratings range from 200 W to 350 W under ideal sunlight and temperature conditions.
Solar Arrays Construction and Mounting
When solar arrays are installed on a property, they must be mounted at an angle to best receive sunlight. Typical solar array mounts include roof, freestanding, and directional tracking mounts (see Figure 4). Roof-mounted solar arrays can blend in with the architecture of a dwelling and will save yard space.
Roof-mounted solar arrays attach to the roof rafters and are engineered to handle the same forces and climate conditions as the rooftop. Composition shingles are considered the easiest roofing on which to mount solar arrays, while slate and tile roofing materials are often considered the most difficult. The main drawback of roof-mounted solar arrays is that they require access for maintenance.
Freestanding solar arrays can be set at heights that allow convenient maintenance. However, freestanding solar arrays usually require a lot of space. Also, freestanding solar arrays should not be mounted on the ground in areas that receive a lot of snow.
Solar array mounts can also be either fixed or tracking. Fixed solar arrays, which are often roof-mounted or freestanding, are preset for height and angle and do not move with the sun. Directional tracking solar arrays move with the sun from east to west and adjust their angle to maintain the maximum exposure as the sun moves. Directional tracking solar arrays can increase the daily energy output of a PV system from 25% to 40%. However, despite the increased power output, directional tracking arrays may not justify the increased cost due to the complexity of the mounting system.
PV Combiner Boxes
A PV combiner box receives the output of several solar panel strings and consolidates this output into one main power feed that connects to an inverter. PV combiner boxes are normally installed close to solar panels and before inverters. PV combiner boxes can include overcurrent protection, surge protection, pre-wired fuse holders, and preconfigured connectors for ease of installation to the inverter. The use of pre-wired connectors saves running wires to the inverter. PV combiner boxes should be inspected periodically for leaks or loose connections.
PV combiner boxes are not required for every PV system installation. For example, when there are only two or three strings of solar panels, a combiner box may not be required. In these cases, the strings of solar panels are connected directly to the inverter.
PV Inverters
An inverter is a device that receives DC power and converts it to AC power. PV inverters serve three basic functions: they convert DC power from the PV panels to AC power, they ensure that the AC frequency produced remains at 60 cycles per second, and they minimize voltage fluctuations. The most common PV inverters are micro-inverters, string inverters, and power optimizers (See Figure 5).
A microinverter is a device that converts DC power to AC power and is mounted directly to individual solar panels. Because the DC to AC conversion happens at each solar panel, the microinverters maximize the potential output of a system. For example, if one solar panel is shaded by a tree, it will not affect the output of any other solar panels. Microinverters also eliminate the need for potentially hazardous high-voltage DC wiring.
A string inverter is a device that converts DC power to AC power from several solar panels that are connected in series. However, in a series configuration, if one of the solar panels stops producing electricity, even due to temporary shading, it can decrease the performance of the whole system. String inverters are in the high-voltage range (600 V to 1000 V) and are used with large PV systems with no shading concerns. Usually, only one string inverter is needed for a residential application.
A power optimizer (maximizer) is a hybrid microinverter system that conditions the DC power before sending it to a centralized inverter instead of converting the DC power from the solar panels directly into AC power. Power optimizers, like microinverters, still perform well when one or more panels are shaded or when panels are installed facing different directions. Power optimizer systems tend to cost more than string inverter systems but less than microinverter systems.
PV Disconnects
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components of PV systems from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. Disconnects ensure that the PV system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance or repair. With grid-connected PV systems, safety disconnects ensure that the generating equipment is isolated from the grid for the safety of utility personnel. A disconnect is needed for each source of power or energy storage device in the PV system. An AC disconnect is typically installed inside the home before the main electrical panel. Utilities commonly require an exterior AC disconnect that is lockable and mounted next to the utility meter so that it is accessible to utility personnel.






